Explore our network of country and industry based websites to access localized information, product offerings, and business services across our group.
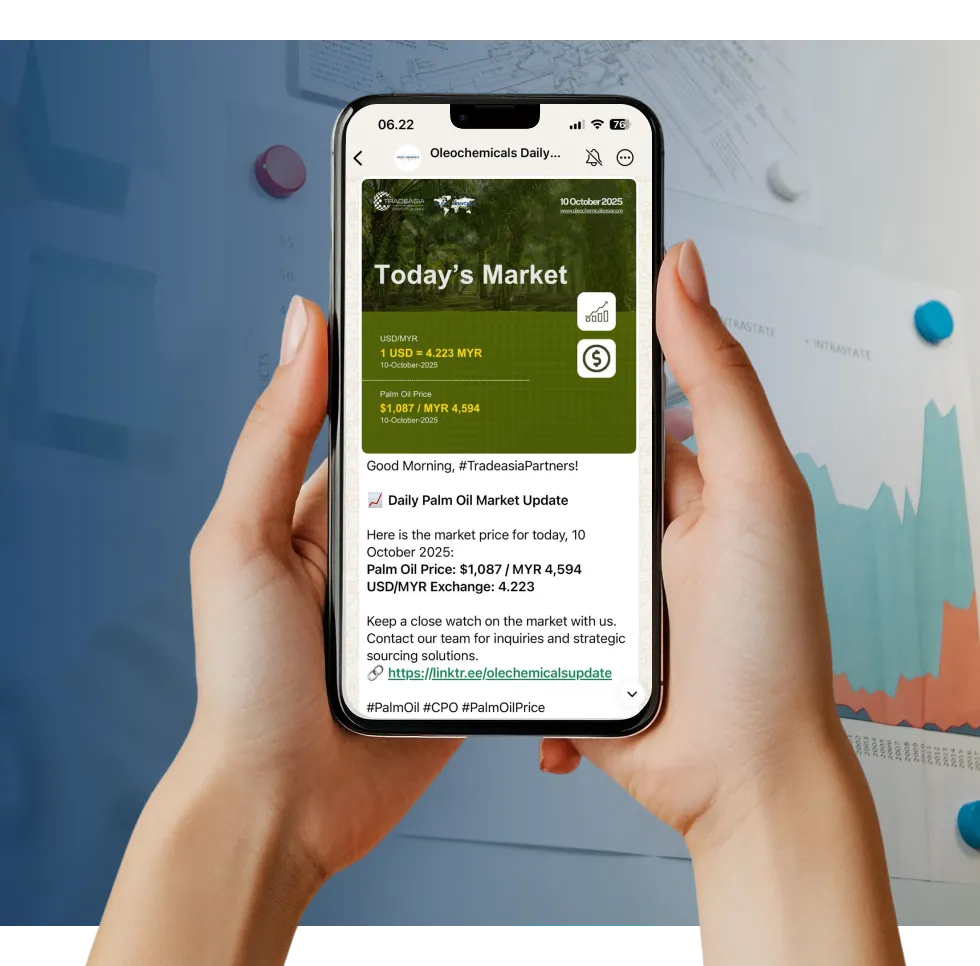
Access reliable chemical market information through our update channels.
Real-time Updates
Daily Updates
Log in to start sending quotation requests for any product.
Don't have an account? Sign Up Here
Log in now to access technical product documents from our product range.
Don't have an account? Sign Up Here
Home All Products Xanthan Gum - Thailand
|
IUPAC Name |
: - |
|
Cas Number |
: 11138-66-2 |
|
HS Code |
: 3913.90.20.15 |
|
Formula |
: C35H49O29 |
|
Appearance Name |
: Off white powder |
|
Common Names |
: Corn Sugar Gum |
|
Packaging |
: 25kg/bag |
For more detailed information including pricing, customization, and shipping:
Brief Overview
Xanthan gum is a polysaccharide composed of glucose, mannose, and glucuronic acid molecules. It can be obtained from different sources, including corn, wheat, and soy. The viscosity of a liquid increases with a higher weight ratio of added xanthan gum. Typically, a concentration of 0.2% by weight is recommended, as an excess of xanthan gum can lead to an undesirable slimy texture. Xanthan gum exhibits stable performance across a range of viscosities, temperatures, and pH levels.
Manufacturing Process
Xanthan gum is created through the fermentation of glucose, sucrose, and lactose. The resulting polysaccharide is extracted from the growth medium using isopropyl alcohol and then finely ground into a powder during the fermentation process. This fine powder is introduced into a liquid medium to produce the gum. In an industrial setting, xanthan gum is manufactured by introducing a sterile aqueous solution containing carbohydrates, a nitrogen source, dipotassium phosphate, and trace elements. Following fermentation, the polymer is precipitated from the medium by the addition of isopropyl alcohol.
Food Industry
Xanthan gum finds extensive application as a food additive across the food industry. Its role as a thickening agent is crucial in maintaining the viscosity of pastry fillings, preventing water seepage that could compromise the dough's integrity and crispness. In ice creams, xanthan gum is employed to hinder the formation of ice crystals, contributing to a smoother texture. Its versatile usage extends to frozen foods, beverages, and egg substitutes crafted from egg whites, where it replaces the fat and emulsifiers present in yolks. Beyond this, xanthan gum plays a key role in a variety of food products, including salad dressings, sauces, instant items, desserts, bakery goods, dairy products, fruit juices, and the creation of various low-calorie foods.

